In the realm of natural remedies, aromatherapy stands out as a fragrant haven, where essential oils unlock a symphony of therapeutic benefits. Our comprehensive aromatherapy chart sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Embarking on this aromatic journey, we delve into the essence of essential oils, exploring their therapeutic properties and recommended uses. We meticulously craft an aromatherapy blend chart, categorizing essential oil combinations based on specific purposes, from relaxation to rejuvenation. Unraveling the mysteries of aromatherapy application methods, we illuminate the benefits and precautions of inhalation, topical use, and diffusion.
Aromatherapy Essential Oils
Aromatherapy utilizes various essential oils extracted from plants to promote physical and emotional well-being. These oils possess therapeutic properties and are commonly used in diffusers, baths, or topical applications.
The following is a comprehensive list of essential oils frequently employed in aromatherapy, along with their therapeutic properties and recommended uses:
Bergamot Oil
- Therapeutic Properties:Uplifting, calming, reduces stress and anxiety.
- Recommended Uses:Diffusion, baths, massage blends.
Chamomile Oil
- Therapeutic Properties:Soothing, anti-inflammatory, promotes relaxation.
- Recommended Uses:Diffusion, baths, topical application for skin irritation.
Eucalyptus Oil
- Therapeutic Properties:Decongestant, antibacterial, promotes clear breathing.
- Recommended Uses:Diffusion, steam inhalation, chest rubs.
Lavender Oil
- Therapeutic Properties:Relaxing, promotes sleep, reduces stress and anxiety.
- Recommended Uses:Diffusion, baths, massage blends, sleep pillows.
Lemon Oil
- Therapeutic Properties:Uplifting, energizing, improves mood.
- Recommended Uses:Diffusion, household cleaning, air fresheners.
Peppermint Oil
- Therapeutic Properties:Stimulating, improves focus and concentration.
- Recommended Uses:Diffusion, topical application for headaches and muscle pain.
Tea Tree Oil
- Therapeutic Properties:Antibacterial, antifungal, promotes skin health.
- Recommended Uses:Topical application for acne, skin infections, and dandruff.
Aromatherapy Blends
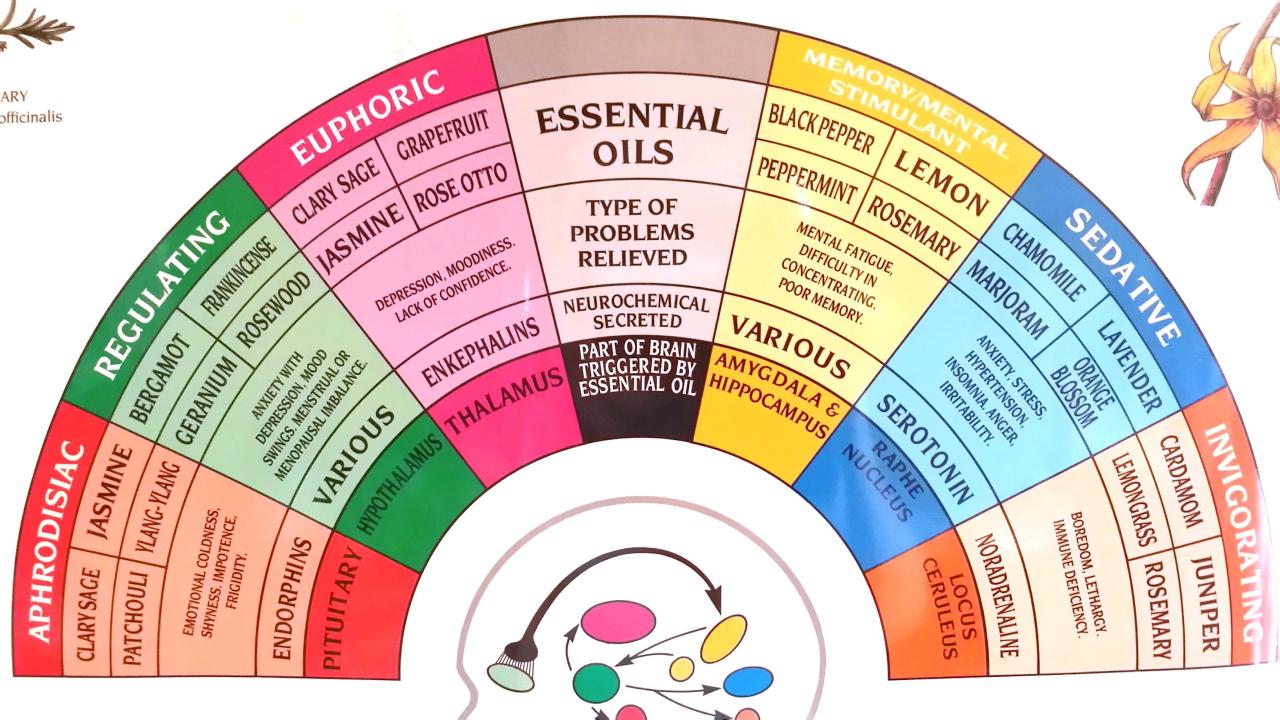
Aromatherapy blends are combinations of essential oils that are designed to work together to achieve a specific purpose. These blends can be used for a variety of purposes, including relaxation, energy boost, sleep aid, and more.
When creating an aromatherapy blend, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The purpose of the blend
- The essential oils that will be used
- The proportions of each essential oil
Once you have considered these factors, you can begin to create your own aromatherapy blends. Here are a few tips for creating effective blends:
- Start with a small number of essential oils (2-3). As you become more experienced, you can experiment with more complex blends.
- Use high-quality essential oils. This will ensure that your blends are effective and safe.
- Follow the recommended proportions for each essential oil. This will help you to create a balanced blend that is not too strong or too weak.
- Test your blends on a small area of skin before using them on a larger area. This will help you to avoid any allergic reactions.
Relaxation Blends
Relaxation blends are designed to help you to relax and de-stress. These blends can be used to promote sleep, reduce anxiety, and relieve tension.
Some of the most common essential oils used in relaxation blends include:
- Lavender
- Chamomile
- Ylang-ylang
- Bergamot
- Clary sage
Here is a simple relaxation blend that you can try:
- Lavender (5 drops)
- Chamomile (3 drops)
- Ylang-ylang (2 drops)
This blend can be used in a diffuser, added to a bath, or applied to the skin.
Aromatherapy Application Methods
Aromatherapy offers a diverse range of application methods, each with its unique benefits and precautions. Understanding these methods empowers you to tailor your aromatherapy experience to your specific needs and preferences.
Inhalation
Inhalation is a direct and effective way to experience the therapeutic effects of essential oils. By breathing in the volatile compounds released from essential oils, you can target the respiratory system, promote relaxation, and enhance mood.
- Direct Inhalation:Inhale the scent of essential oils directly from the bottle or diffuser.
- Steam Inhalation:Add a few drops of essential oils to a bowl of hot water and inhale the steam.
- Nasal Inhalers:Use a nasal inhaler containing essential oils for quick relief from congestion or respiratory issues.
Precautions:Avoid direct inhalation of undiluted essential oils, as they can irritate the respiratory tract. Always dilute essential oils in a carrier oil or water before inhalation.
Topical Use
Topical application involves applying essential oils directly to the skin, allowing them to be absorbed locally. This method is beneficial for targeting specific areas of the body, promoting skin health, and reducing inflammation.
- Massage:Dilute essential oils in a carrier oil and massage into the skin.
- Bathing:Add a few drops of essential oils to a warm bath for relaxation or detoxification.
- Compresses:Soak a cloth in a solution of essential oils and water and apply it to the affected area.
Precautions:Some essential oils are potent and can cause skin irritation. Always dilute essential oils in a carrier oil before topical use, and perform a patch test on a small area of skin before applying it to larger areas.
Diffusion
Diffusion disperses essential oils into the air, creating an aromatic atmosphere that can enhance mood, promote relaxation, and purify the air. This method is ideal for large spaces or when you want to create a subtle and long-lasting effect.
- Electric Diffusers:These devices use ultrasonic waves to create a fine mist of essential oils and water.
- Candle Diffusers:Essential oils are heated by a candle flame, releasing their scent into the air.
- Reed Diffusers:Essential oils are absorbed by reeds and slowly released into the air.
Precautions:Avoid using diffusers for extended periods or in small, enclosed spaces, as this can lead to excessive exposure to essential oils. Ensure the diffuser is placed in a well-ventilated area.
Aromatherapy Safety Guidelines
Essential oils are potent plant extracts that can provide numerous therapeutic benefits when used safely and appropriately. However, it’s crucial to adhere to certain safety guidelines to minimize potential risks and ensure a positive aromatherapy experience.
Dilution Ratios
- For topical applications, essential oils must be diluted with a carrier oil, such as jojoba, coconut, or almond oil, to prevent skin irritation. The recommended dilution ratio varies depending on the oil and intended use, but a general guideline is 2-5% dilution (2-5 drops of essential oil per 10ml of carrier oil).
Contraindications
- Certain essential oils are not suitable for everyone. For example, pregnant women, infants, and individuals with certain medical conditions should consult a healthcare professional before using aromatherapy.
- Some essential oils, such as tea tree oil and eucalyptus oil, can be toxic if ingested and should never be taken internally.
Storage Recommendations
- Essential oils should be stored in dark glass bottles to protect them from light and heat, which can degrade their potency and quality.
- Keep essential oils out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or exposure.
Aromatherapy Research and Evidence
A growing body of scientific research supports the therapeutic benefits of aromatherapy. Clinical studies have shown that essential oils can effectively alleviate a wide range of physical and emotional conditions.
Clinical Studies
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of aromatherapy in various areas, including:
- Pain management:Lavender and peppermint essential oils have been shown to reduce pain intensity and improve sleep quality in patients with chronic pain.
- Anxiety and depression:Inhaling essential oils of bergamot, lavender, and chamomile has been found to reduce anxiety and depressive symptoms.
- Nausea and vomiting:Peppermint and ginger essential oils have been effective in reducing nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy and motion sickness.
- Cognitive function:Rosemary and lemon essential oils have been shown to improve cognitive function and memory in older adults.
- Skin health:Tea tree oil and lavender essential oil have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, making them beneficial for treating acne and other skin conditions.
Scientific Evidence
The therapeutic effects of essential oils are attributed to their complex chemical composition. These compounds interact with various receptors in the body, influencing physiological and psychological processes.
- Anti-inflammatory effects:Essential oils like frankincense and turmeric contain compounds that inhibit inflammation and reduce pain.
- Sedative effects:Lavender and chamomile essential oils promote relaxation and sleep by activating GABA receptors in the brain.
- Stimulating effects:Rosemary and peppermint essential oils have stimulating effects on the nervous system, improving alertness and cognitive function.
- Antimicrobial effects:Tea tree oil and oregano essential oil have powerful antimicrobial properties, making them effective against bacteria and fungi.
Overall, the scientific evidence suggests that aromatherapy can be a valuable complementary therapy for various health conditions. However, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before using essential oils, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Last Recap
As we conclude our aromatic exploration, we unravel the scientific tapestry of aromatherapy, examining research and clinical studies that validate its therapeutic prowess. Our comprehensive guide empowers you with the knowledge and tools to harness the transformative power of essential oils, unlocking a world of well-being and vitality.